With the gradual reduction of solar subsidies worldwide, the return on investment for pure photovoltaic projects is declining. This has made solar-plus-storage systems an increasingly attractive choice for homeowners. Policy support has already catalyzed the residential energy storage market in countries like Australia and Germany. Most industry experts agree that the trajectory for energy storage will mirror that of solar PV: initial high costs followed by price reductions and market expansion driven by economies of scale.
For many in the industry, residential energy storage remains a new frontier. At Chasun, we frequently receive inquiries about how these systems function. This guide provides a clear, technical explanation of the integrated residential energy storage system.
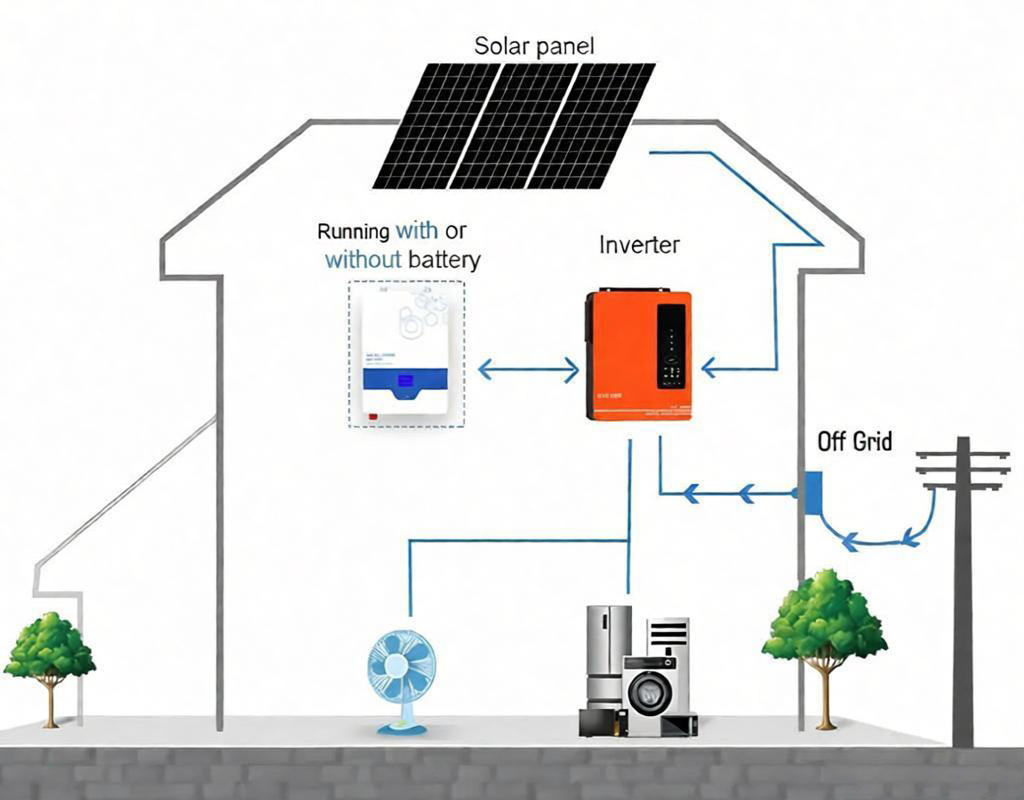
An integrated residential energy storage system combines the solar inverter, battery, and controller into a single, compact unit. It typically features a user-friendly touchscreen for intuitive status display, parameter adjustment, and switching between multiple operational modes.
How It Works: System Architecture
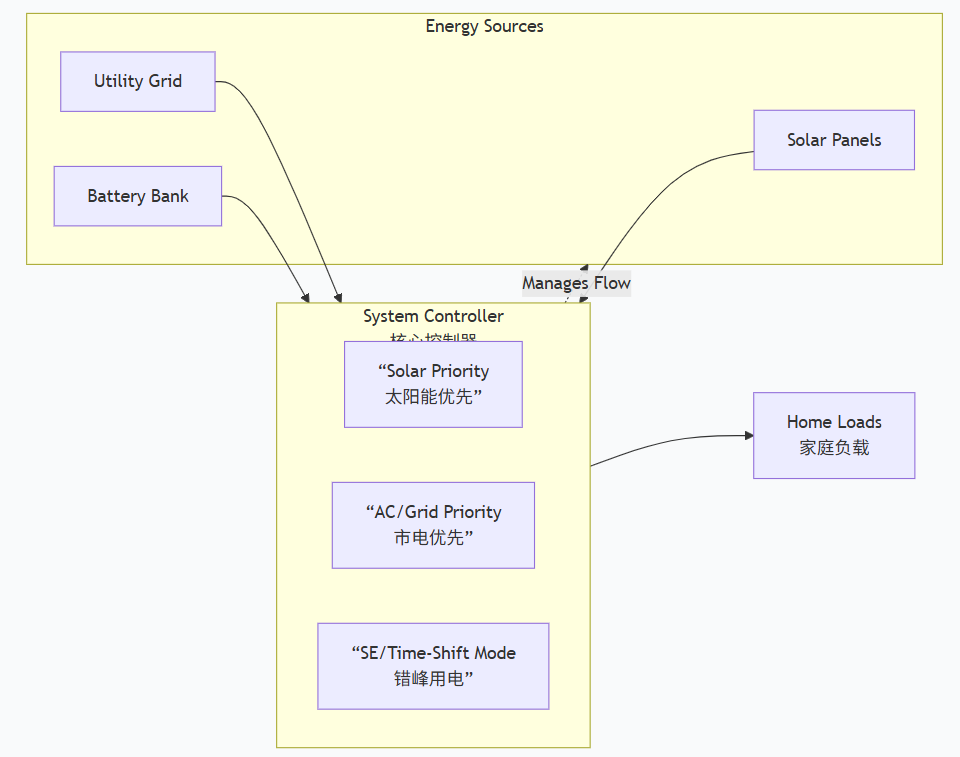
The core of the system is its intelligent management of energy flow between four key components: solar panels, the battery bank, the home’s electrical loads, and the utility grid. The system controller acts as the brain, directing power according to the selected mode.
The following diagram illustrates the primary energy flow paths within a typical integrated residential energy storage system:
Operational Modes Explained
The system’s intelligence lies in its configurable operating modes, allowing homeowners to optimize for self-consumption, backup security, or cost savings.
A. Solar Priority Mode
In this mode, the system maximizes the use of solar energy. The logic flow is as follows:
- Primary Source: Solar power is the first priority for powering home loads.
- Excess Solar: Any surplus solar energy charges the battery bank.
- Solar Shortfall: If solar generation is insufficient, the battery supplements the power to the loads.
- Low Battery & Grid Intervention: If the battery’s State of Charge drops to 10% or below, the system automatically switches the loads to the utility grid. The grid and solar will then charge the battery simultaneously until full, after which the system reverts to solar/battery power.
- Grid Outage & Critical Low Battery: If the grid is down and the battery is critically low, the system will disconnect non-essential loads. Solar energy will charge the battery until it reaches 40% SOC, at which point load supply resumes.
B. AC (Grid) Priority Mode
This mode prioritizes grid power, treating the battery as a backup.
- Primary Source: The utility grid powers the home loads when the battery is sufficiently charged.
- Grid Charging: If the battery is low, the grid (along with any available solar) charges it.
- Grid Failure: During a grid outage, the system automatically switches to solar power for the loads, using the battery to supplement any shortfall.
C. SE Priority Mode (Time-of-Use / Load Shifting)
This intelligent mode is designed for regions with variable electricity tariffs to maximize bill savings.
- User-Defined Schedule: The homeowner sets a specific time window (e.g., 1:00 AM – 6:00 AM).
- Scheduled Grid Use: During this window, the home loads are powered by the (cheaper) grid electricity. The grid and solar simultaneously charge the battery.
- Scheduled Battery Use: Outside the set window, the system operates in a solar-priority manner, using solar and battery power to run the home and avoid expensive peak grid rates.
- Purpose: This allows users to “charge cheap, use smart,” storing low-cost off-peak energy to avoid drawing power from the grid during high-cost peak periods.
Conclusion
Compared to traditional grid-tied solar systems, integrated residential energy storage involves a higher initial investment and more complex installation. However, it offers significantly broader applications and more powerful functionality, including backup power and intelligent energy management.
As the cost of storage continues to fall, solar-plus-storage systems are becoming increasingly economical. We at Chasun believe that the residential energy storage market is poised for significant growth and innovation in the near future.
Ready to design your custom energy storage solution?
[Contact Chasun’s Experts Today] for a tailored system design and quote.
Post time: Dec-04-2025