Energy Storage Systems (ESS) play a critical role in modern solar projects by balancing power generation, consumption, and grid interaction.
To fully understand solar + storage solutions, it is essential to first understand how an ESS works at a system and energy level.
1. What Is an Energy Storage System (ESS)?
An Energy Storage System stores electrical energy when generation exceeds demand and releases it when demand exceeds generation.
In solar applications, ESS primarily serves to:
-
Improve energy utilization
-
Reduce grid dependence
-
Enhance power reliability
2. Core Components of an ESS
A typical ESS consists of:
-
Battery system (energy storage medium)
-
Battery Management System (BMS)
-
Power Conversion System (PCS)
-
Energy Management System (EMS)
Each layer controls a different aspect of energy flow and safety.
3. How Energy Is Stored: The Basic Energy Formula
The amount of energy stored in a battery system is calculated as:
Energy (kWh)=Battery Capacity (Ah)×Nominal Voltage (V)÷1000
Example:
A battery system rated at 200 Ah with a 512 V nominal voltage:
200×512÷1000=102.4 kWh
This formula is fundamental when designing ESS capacity for real projects.
4. Charging & Discharging Logic in Solar + ESS Systems
Charging Process
-
Solar PV generates electricity during daylight
-
Loads consume power first
-
Excess energy charges the battery
Discharging Process
-
Solar output decreases or demand increases
-
Battery discharges stored energy
-
Grid usage is reduced or avoided
Diagram 1: Solar + ESS Energy Flow
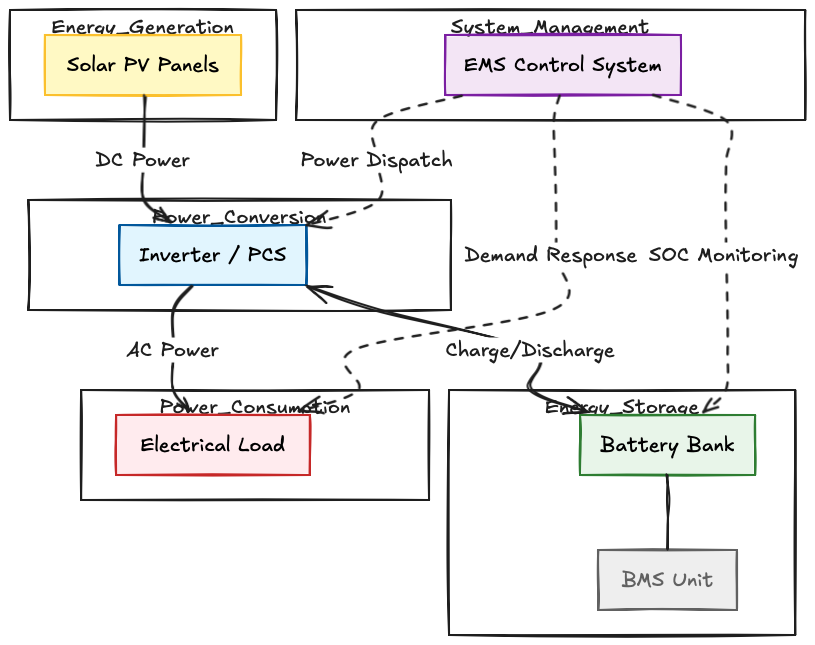
This simplified flow illustrates how energy moves between generation, storage, and consumption.
5. State of Charge (SOC): The Core ESS Indicator
State of Charge (SOC) indicates the remaining energy in a battery.
Example:
-
Total capacity: 100 kWh
-
Remaining energy: 60 kWh
SOC=60%
Most systems operate within a controlled SOC window to extend battery life.
6. Why ESS Performance Depends on PV Module Efficiency
ESS does not generate energy—it stores it.
Therefore, the quality and efficiency of the PV system directly impact ESS performance.
High-efficiency PV modules generate:
-
More usable surplus energy
-
Faster battery charging
-
Better system economics
This is why solar + storage projects often pair ESS with high-efficiency modules such as Jinko Tiger Neo 3.0.
Related high-efficiency PV solutions:
7. ESS as the Bridge Between Solar and Real-World Demand
Energy storage systems transform intermittent solar generation into stable, dispatchable power, making solar viable for:
-
Commercial & industrial users
-
Grid-constrained regions
-
Hybrid and off-grid systems
Understanding ESS fundamentals is essential before selecting system size, battery type, or application scenario.
Conclusion
Energy Storage Systems operate through controlled charging, discharging, and intelligent energy management.
When combined with high-efficiency PV generation, ESS becomes a powerful tool for improving energy reliability and economic performance.
Post time: Feb-04-2026

